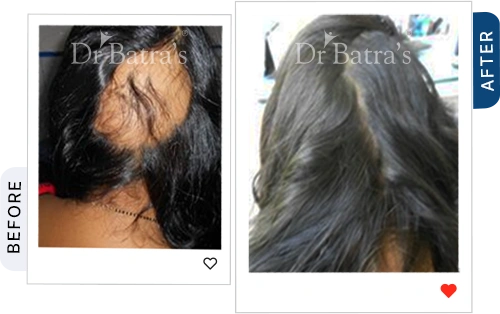
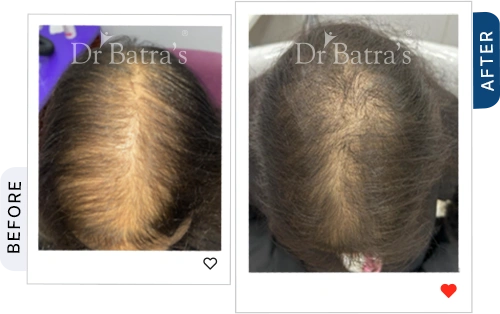
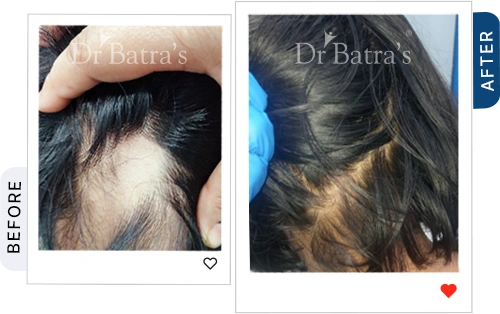
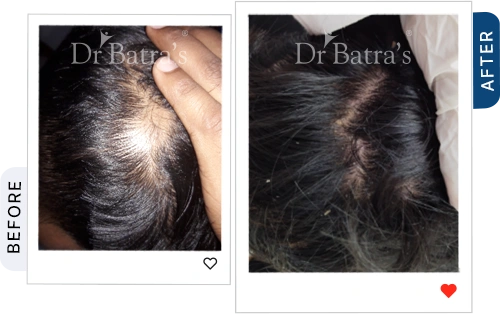
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a growing concern among both men and women. Whether it's patchy bald spots, gradual thinning, or sudden shedding, different types of alopecia require different approaches for diagnosis and treatment. The key to managing hair loss effectively is early intervention and understanding its root cause.
This blog explores alopecia types, symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options, including homeopathy, which offers a holistic, long-term solution to hair loss.
What is Alopecia?
Alopecia refers to hair loss caused by various factors, including genetics, autoimmune conditions, and lifestyle triggers. According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information, nearly 2% of the global population is affected by alopecia areata.
The condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss in small patches. Alopecia can affect not only the scalp but also the eyebrows, eyelashes, and other body parts.
Discover the Causes of Alopecia Areata and its impact.
Dr Batra’s® pro tip:
Avoid harsh chemical treatments or over-styling if you're facing hair fall. Gentle care and personalised homeopathy work best
Different Types of Alopecia
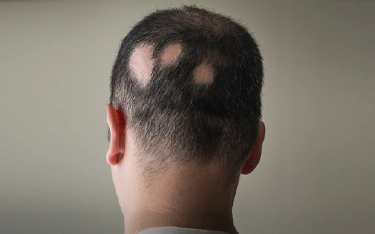
Alopecia Areata (Patchy Hair Loss)
Alopecia Areata causes small, round bald patches on the scalp or other areas of the body. It is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles.
Advanced Forms of Alopecia Areata
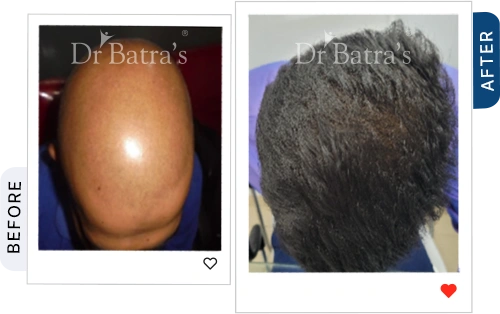
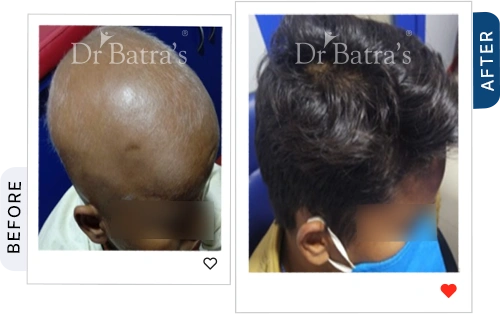
Alopecia Totalis
- Complete hair loss on the scalp.
- Affects around 5% of alopecia patients (International Journal of Trichology, 2019).
Alopecia Universalis
- The rarest form causes complete body hair loss, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and chest hair.
- Affects less than 1% of alopecia patients.
Diffuse Alopecia Areata
- Hair thinning occurs all over the scalp instead of in specific patches.
Explore Alopecia Areata in Children for early detection.
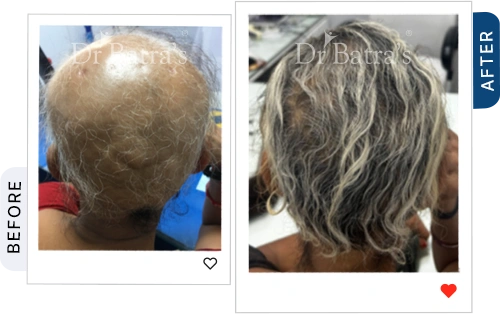
Androgenetic Alopecia (Pattern Hair Loss)
- The most common form of hair loss in men and women.
- In women, it worsens the parting and overall hair thinning.
- In men, it leads to a receding hairline and bald spots.
Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia)
- Hair follicles are replaced by scar tissue.
- Often associated with skin conditions and severe inflammation.
- Irreversible hair loss requires early diagnosis to prevent progression.
Temporary and Lifestyle-Induced Alopecia
Telogen Effluvium (Stress-Induced Hair Loss)
- Diffuse hair thinning due to extreme stress, pregnancy, surgery, or illness.
- Usually reversible once the underlying cause is managed.
Chemotherapy-Induced Alopecia (Anagen Effluvium)
- Rapid hair loss caused by chemotherapy drugs or strong medications.
- Hair regrowth usually resumes after stopping treatment.
Postpartum Alopecia
- Hormonal hair loss after childbirth, occurring 2-3 months post-delivery.
- Usually temporary, with regrowth occurring within a year.
Traction Alopecia (Due to Tight Hairstyles)
- Hair loss due to tight ponytails, braids, or hair extensions.
- It can become permanent if the hair follicles are severely damaged.
Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder)
- Compulsive hair-pulling from the scalp, eyebrows, or eyelashes.
- Often linked to Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
Learn more about Alopecia in Women and how to manage it.
What Does Alopecia Look Like?
Hair loss can manifest differently in each individual:
- Small bald patches that regrow and fall out repeatedly.
- Gradual thinning across the scalp.
- Sudden hair shedding in large amounts.
- Complete loss of hair from the scalp or body.
Learn about the symptoms of alopecia areata