FAQs
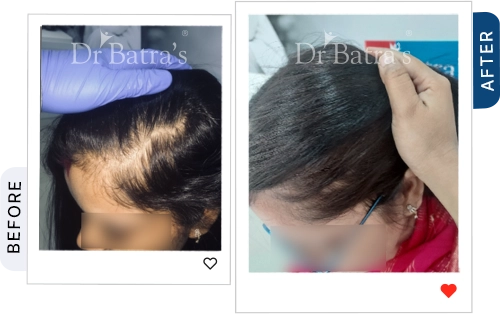
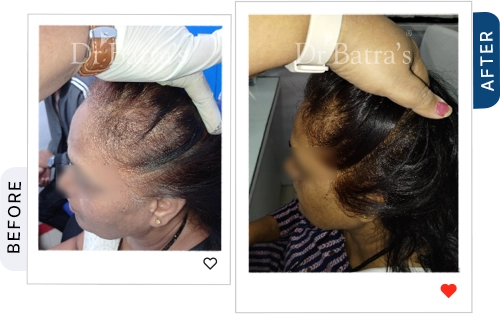
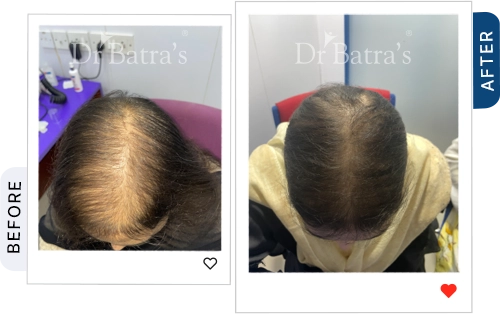
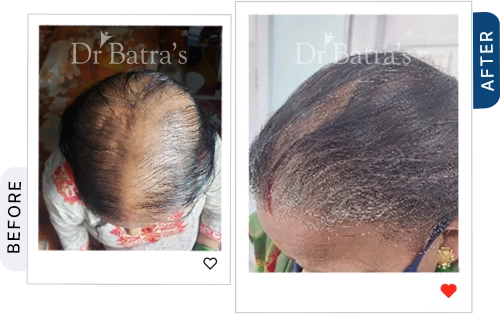
The first stage involves gradual thinning near the parting line, increased hair shedding, and weaker hair strands. Over time, the central part widens, and the scalp may become more visible, especially under bright light.
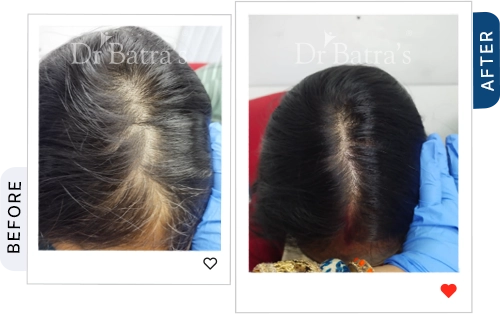
You may notice a visible widening of your center parting, thinning around the crown, and less volume on top compared to the sides and back. The scalp often looks more exposed under light.
Yes, chronic stress can trigger hormonal imbalances and accelerate hair shedding in genetically prone individuals. It’s essential to manage stress alongside treatment for better results.
Yes, homeopathy works best in early stages by addressing hormonal imbalances and stimulating hair follicles naturally. It can slow progression, improve hair quality, and prevent further thinning without side effects.