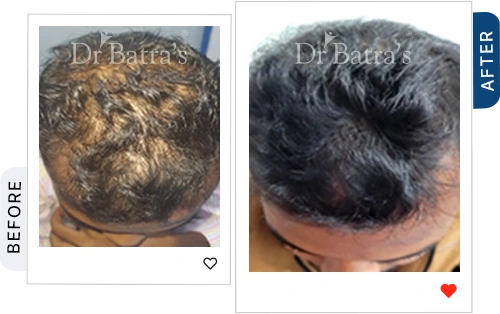
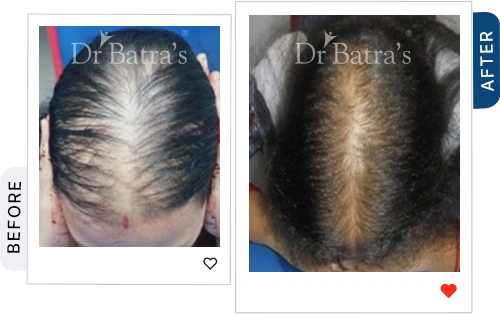
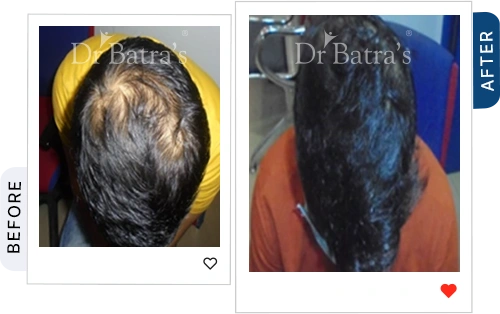
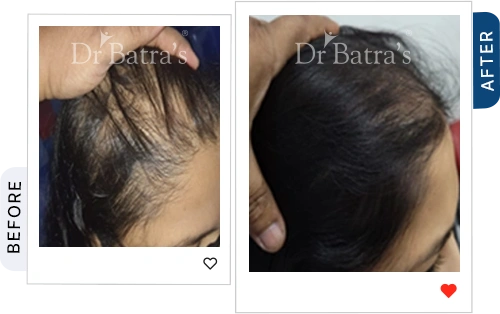
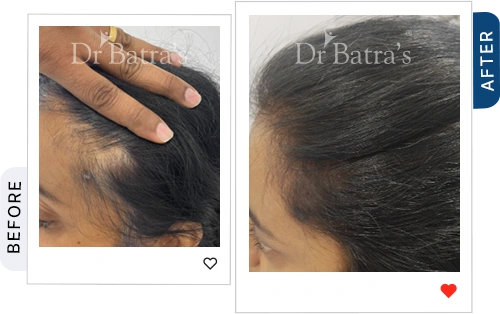
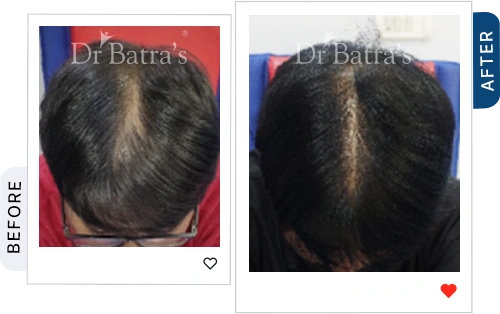
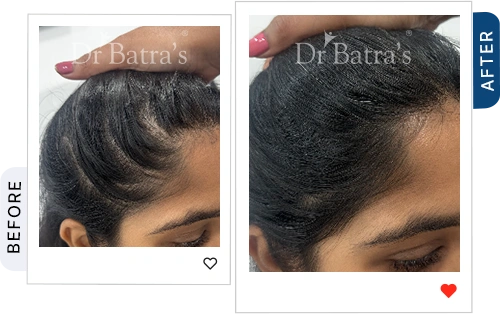
FAQs
What are the first signs of hair loss and balding?
Increased shedding, receding hairline, thinning at the crown, and a widening hair part are early signs to watch for.
Can stress cause sudden hair loss?
Yes, both emotional and physical stress can trigger sudden hair shedding, known as telogen effluvium.
How do I know if my hair fall is excessive?
Losing more than 100 strands daily, visible thinning, and frequent breakage while combing may indicate excessive hair fall.
Are itchy or flaky scalp signs of hair loss?
Yes, scalp irritation can signal underlying conditions like dandruff or inflammation that may lead to hair loss.
Can hair texture change be an early sign of hair fall?
Absolutely. Hair becoming finer, dull, or weaker can be an early symptom of thinning and potential hair loss.