Tattoos have long been a form of self-expression and body art, but if you have vitiligo disease, you might wonder: Is it safe to get a tattoo? Can tattooing worsen vitiligo or lead to further skin depigmentation? Understanding the risks, precautions, and alternatives is essential before making this decision.
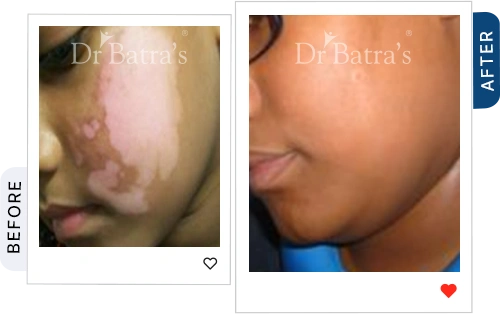
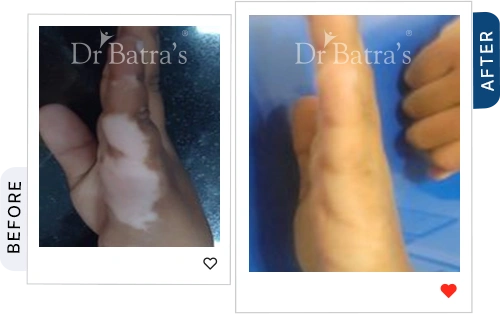
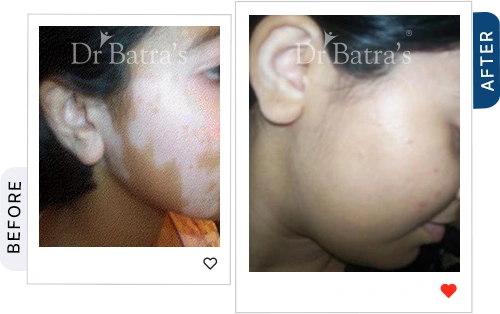
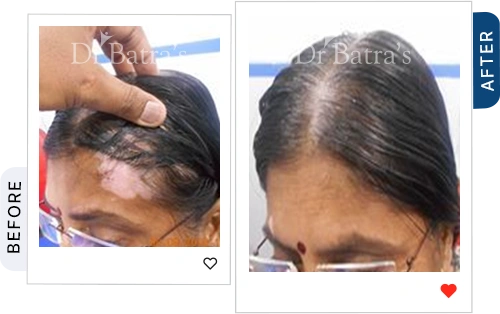
A government-backed review found that medical tattooing for vitiligo can be safe and effective when done on stable patches, with high patient satisfaction and no major side effects (NIH). At Dr Batra’s®, we assess vitiligo stability before recommending micropigmentation,a gentler alternative to tattoos, and combine it with personalised homeopathy treatment for vitiligo to improve skin tone, boost immunity, and protect long-term skin health.
What is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is an autoimmune skin condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells. This leads to patchy white spots on the skin due to the loss of melanin.
- Commonly affected areas: Face, hands, arms, legs, and genital regions.
- Triggers: Autoimmune disorders, genetics, sun exposure, or skin trauma.
- Progression: Vitiligo can spread unpredictably over time.
Dr Batra’s® pro tip:
If you have vitiligo, avoid tattooing over areas that are changing. Stability, sun protection, and gentle aftercare are key, homeopathy can further help preserve skin tone.
Can You Tattoo Over Vitiligo?
Technically, yes, but it comes with potential risks. Tattooing vitiligo-affected skin may not have the same outcome as tattooing normal skin due to:
- Ink absorption differences : Pigment may not settle evenly, leading to inconsistent results.
- Possible new vitiligo patches : Trauma from tattooing can trigger new vitiligo spots (Koebner phenomenon).
- Color matching difficulties : Skin tone varies over time, making color-matching tattoos challenging.
Why Do People with Vitiligo Get Tattoos?
People with vitiligo may seek tattoos for different reasons:
- To cover depigmented patches with skin-tone ink.
- To create artwork that embraces vitiligo as part of their identity.
- To boost self-confidence by reducing visible contrast between pigmented and non-pigmented skin.
Is Tattooing Safe for Vitiligo Patients?
There are several concerns to consider before getting a tattoo if you have vitiligo:
- Spreading of vitiligo : Tattoo trauma might cause new white patches near the tattooed area.
- Ink reaction : Some people with vitiligo may experience inflammation, irritation, or allergic reactions.
- Color mismatch : Over time, skin pigment changes can make tattoos appear unnatural or faded.
Micropigmentation vs. Traditional Tattoo
If you want a tattoo to blend with your skin, micropigmentation is a better alternative to traditional tattooing.
Micropigmentation (Medical Tattooing)
- Uses semi-permanent ink to camouflage vitiligo spots.
- Typically performed by dermatologists or trained professionals.
- More precise color matching compared to traditional tattoos.
- Results fade over time, requiring touch-ups.
Traditional Tattooing
- Uses permanent ink that does not fade easily.
- Ink may look different over time as skin tone changes.
- Higher risk of vitiligo spreading due to needle trauma.
Which Is Better?
- If vitiligo is stable : Micropigmentation may be a safer option.
- If vitiligo is active : Tattooing is not recommended, as new patches can form.