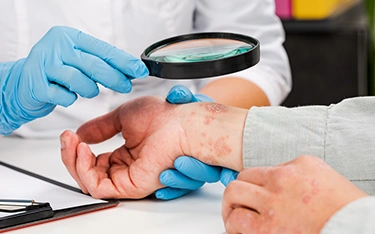
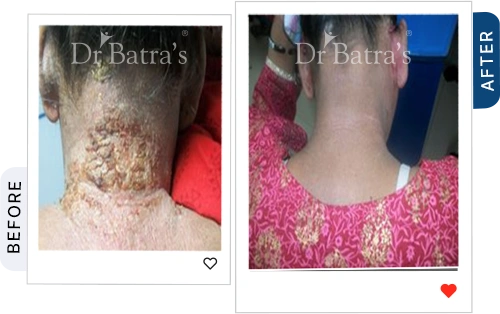
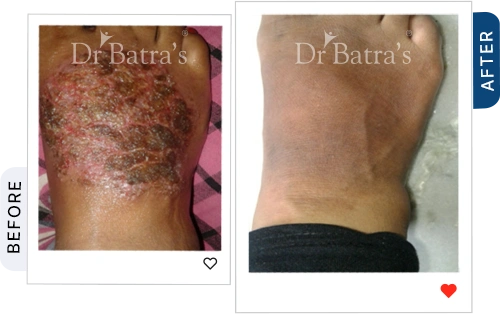
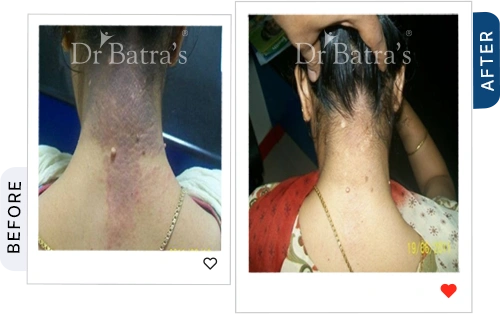
If your skin constantly feels itchy, red, or flaky, there’s a chance it could be eczema. Often mistaken for dryness, many people struggle to tell the difference between eczema vs dry skin. In reality, eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition triggered by genetics, allergies, immune response, and environmental irritants.
It affects 15% of children and around 10% of adults in India, according to the Indian Dermatology Society (2023). Common eczema symptoms include persistent itching, redness, and flare-ups that interfere with daily comfort. Though not contagious, eczema can worsen without timely care, leading to thickened, cracked skin or even secondary infections.
This blog will guide you on how to recognise early eczema symptoms, when to seek help, and practical ways to keep it under control, naturally and safely.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Eczema
- Persistent itching, often starting before a visible rash appears
- Red and inflamed patches of skin
- Dry, cracked, or scaly texture, especially after bathing
- Small raised bumps that may ooze fluid and form a crust
- Thickened or leathery skin over time due to repeated scratching
Learn about common causes of eczema
Types of Eczema Symptoms by Area
-
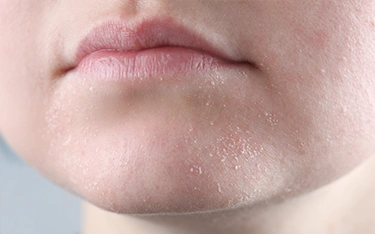
Face and Neck
- Flaky cheeks and jawline
- Itchiness that worsens after sun or soap exposure
- Swelling or skin darkening over time
-
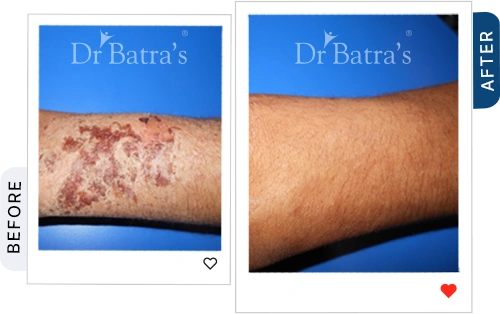
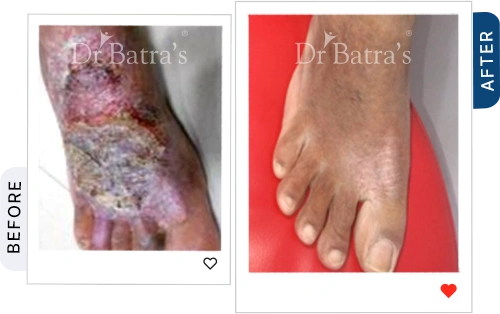
Hands, legs and Feet
- Cracks between fingers or on soles
- Raw, burning sensation
- Blisters in severe cases
-
Under-Eye Area
- Swelling, flakiness, and irritation
- Skin sensitivity to cosmetics or sweat
-
Scalp and Behind the Ears
- Dry, crusty scales
- Itchiness and inflammation, often misdiagnosed as dandruff
Compare with Acne: Acne vs Eczema
Eczema Symptoms That Overlap With Other Skin Conditions
|
Condition
|
Overlapping Symptoms with Eczema
|
How Eczema is Different
|
|
Fungal Infections
|
Itching, redness, eczema skin peeling
|
Unlike fungal rashes, eczema symptoms are chronic and may lead to eczema skin shedding and pigmentation changes.
|
|
Psoriasis
|
Scaling, thickened skin, dry patches
|
While psoriasis also causes flaking, dry eczema symptoms often include oozing or exfoliating eczema from irritation.
|
|
Allergic Skin Reactions
|
Redness, itching, rash
|
Allergic rashes fade once the allergen is removed, but eczema is recurring, needing gentle care like exfoliation for eczema and knowing how to exfoliate with eczema safely.
|
|
Dry Skin (vs Eczema)
|
Rough, flaky, itchy skin
|
Simple dryness improves with moisturizers, but dry skin vs eczema differs as eczema causes inflammation, recurring triggers, and long-term eczema skin peeling.
|
Is Skin Shedding a Sure Sign of Eczema?
Eczema skin shedding is not a common sign of eczema. Eczema can be either dry or wet eczema. It is accompanied by redness, itching or irritation and it is best to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
When to Take an Eczema Evaluation Test
You should consider taking aneczema evaluation test if:
- You have recurring dry patches that don’t improve with moisturisers, which could be an early sign of eczema vs dry skin or dry eczema symptoms.
- Itching disrupts your sleep or daily routine, one of the common eczema symptoms.
- Skin flares after stress, diet changes, or weather transitions, often leading to eczema skin shedding or eczema skin peeling.
- You experience sensitivity to fragrances, fabrics, or soaps, making exfoliation for eczema tricky and raising concerns about how to exfoliate with eczema safely.
Dr Batra’s® pro tip:
Don’t ignore the itch, early eczema care prevents flare-ups and long-term skin damage.